Canon Guards
What is a Canon Guard, exactly?
CanonGuard is the Safe’s transaction entrypoint. It enqueues transactions produced by action builders, persists the payload (ABI‑encoded actions), computes the exact Safe transaction hash to approve, verifies which owners have onchain‑approved that hash via approvedHashes, and executes through MultiSendCallOnly once within the allowed window. The Safe’s guard is set to the CanonGuard contract (via the OnlyCanonGuard base), so the Safe rejects any execution not initiated by CanonGuard.
A Safe guard is a hook contract the Safe calls before (and after) every execution. It can allow or reject a transaction based on arbitrary logic.
Canon Guard stores the queued actions immutably at enqueue time; approvals are onchain via SAFE.approveHash(getSafeTransactionHash(...)); and execution is gated by executableAt/expiresAt (short path for pre‑approved builders/hubs; long path otherwise). When emergency mode is enabled, only the configured emergency caller may execute while owners can still propose/approve.
At a glance
- You put transactions in a queue, and they stay exactly as written.
- Owners approve the transaction onchain (no offchain signatures).
- There is a wait: Short for pre‑approved things, longer for new things.
- After the wait, anyone can execute through Canon Guard. If emergency mode is on, only the emergency caller can execute.
Deployment modes: Attached vs detached
You can adopt Canon Guard in two modes.
- Detached (no Safe guard): You do not call
setGuard. Teams use Canon Guard to queue/approve/execute, but the Safe does not enforce it. If Canon Guard has a bug, you can stop using it with no impact on the Safe. This is useful for an initial trial while you validate procedures. - Attached (Safe guard set): You call
setGuard(CanonGuard). The Safe enforces “only Canon Guard may execute”. This closes bypasses and makes approvals uniformly onchain. Risk: a misconfiguration (wrong guard address, incompatible Safe version, or broken guard) can block execution until the guard is changed.
A recommended rollout would be starting detached for a few weeks, verify builders/hubs and team workflow, then attach. Keep a rollback prepared (for example, an action from ChangeSafeGuardActionFactory) to reset the guard if needed.
Breakdown
Roles and responsibilities
CanonGuard.sol(entrypoint): Queue, compute Safe tx hash, collect approved owners, execute viaMultiSendCallOnly.OnlyCanonGuard.sol(Safe guard, inherited): Enforces “execution only via Canon Guard” by rejecting checks where_msgSender != address(this)(the Canon Guard contract).Approver.sol(helper): StandardizesSAFE.approveHash(hash)if approvals are driven via contracts/scripts.
As an example, a lifecycle will look like this:
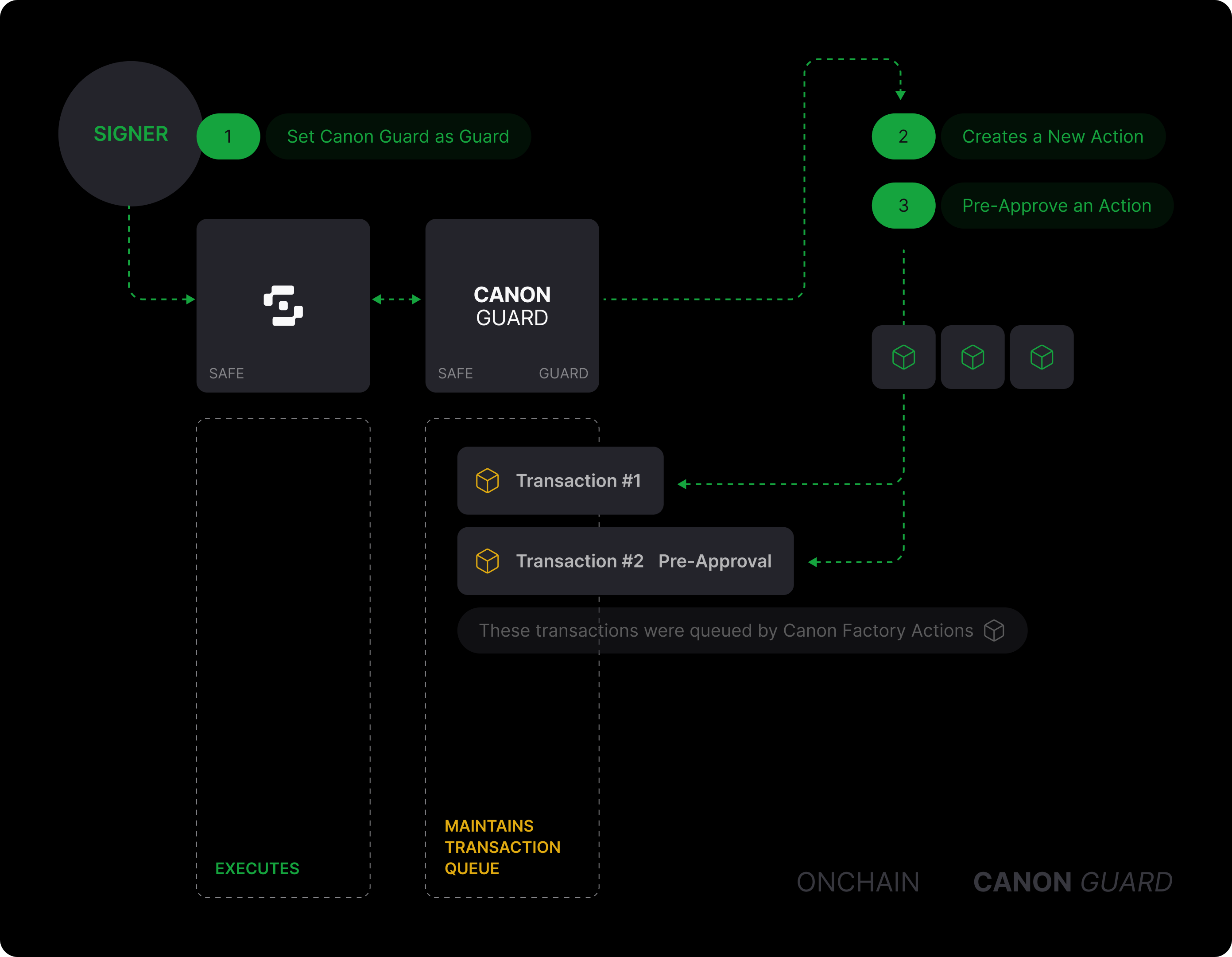
Consider that in this example, we are interacting with the CapTokenTransferHub:
- (1) Set guard (attached mode): Safe is configured with
OnlyCanonGuard, so the Safe only allows executions initiated by the Canon Guard contract. - (2) Optional pre‑approval:
approveActionsBuilderOrHub(hub, duration)lets owners pre‑approve a builder or hub for a limited window, unlocking the short delay path. - (3–4) Create builder: A specific builder is instantiated (e.g.
createNewActionBuilder(token, amount)), and the hub exposes itsAction[]viagetActions(). - (5–7) Queue:
queueTransaction(builder)snapshots the ABI‑encoded actions and setsexecutableAt/expiresAt. The snapshot is immutable; later builder changes don’t affect the queued payload. - Delay window: Execution is blocked until
executableAt. Short if pre‑approved, long otherwise; timing is transparent onchain. - (8) Approvals: Owners approve
getSafeTransactionHash(actions[, nonce])onchain usingSAFE.approveHash(...). Approvals accumulate inapprovedHashes. - (9) Execute: After
executableAtand beforeexpiresAt, callexecuteTransaction(builder)(or batch). Canon Guard assembles approvals and executes viaMultiSendCallOnly. - (10) Effects: The Safe performs the encoded actions atomically (e.g., capped transfers from a hub action).
If circumstances change:
- No‑op:
executeNoActionTransaction()spends a Safe nonce to invalidate stale signatures. - Cancel:
cancelEnqueuedTransaction(actionsBuilder)by the proposer if no approvals exist.
What the Safe guard checks
At checkTransaction(...), OnlyCanonGuard rejects unless _msgSender == address(this) (i.e. the caller seen by Safe is the Canon Guard contract). This closes ad‑hoc or offchain‑driven execution paths.
Emergency mode
With emergency mode set, owners can still queue and approve, but only the configured emergency caller may execute. This adds an additional key for execution under duress.
That’s the whole flow.